Radford A, Metz L, Chintala S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.06434, 2015.
该篇论文提出Deep Convolutional GANs结构 (Figure 1),使用一些方法来提高train稳定性,并通过实验验证
- D的性能
- 可视化D的特征图
- G的Walking in the Latent Space、遗忘性和Vector Arithmetic.

1. 提高训练稳定性的方法
- Stride Conv 替代 Pooling
- Eliminate FC层(相对于GAN中的FC而言)
- BN层,除G的输出层和D的输入层外,否则导致不稳定
- G使用ReLU,输出层使用Tanh。D使用LeakyReLU**
2. 验证D的性能
使用D作为Feature Extractor来classify CIFAR-10和SVHN。
3. D特征图可视化
不同特征图activate on 不同objects (Figure 5) 。

4. Walking in the Latent Space

5. G的遗忘性
G能学到不同object的表达,在second highest Conv层(倒数第二层)的特征上,利用logistic regression 预测activate窗户的filters,比较drop out窗户相关filters与否的生成结果。在drop out窗户filter的生成结果中,一些图片去掉了窗户,一些图片生成相似的其他object,如门、镜子 (Figure 6)。

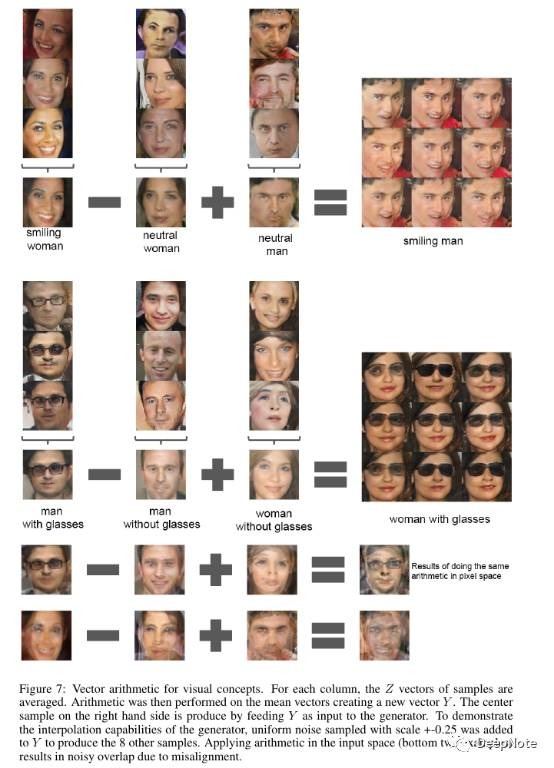
6. Vector Arithmetic of Z
类似于Word2vec of Mikolov (Figure 7)。
Single sample per concept were unstable. Average $Z$ of 3 sample show consistence andstable.
7. Train DCGAN on MNIST
- We found that removing the scale and bias parameters from batchnorm produced better results for both models.
- Noise introduced by batchnorm helps the generative models to better explore and generate from the underlying data distribution.
8. Code
Code comes from github AaronYALai/Generative_Adversarial_Networks_PyTorch.
Code of GAN

Code of DCGAN
